Custom api data
Save new custom api
Basic Info
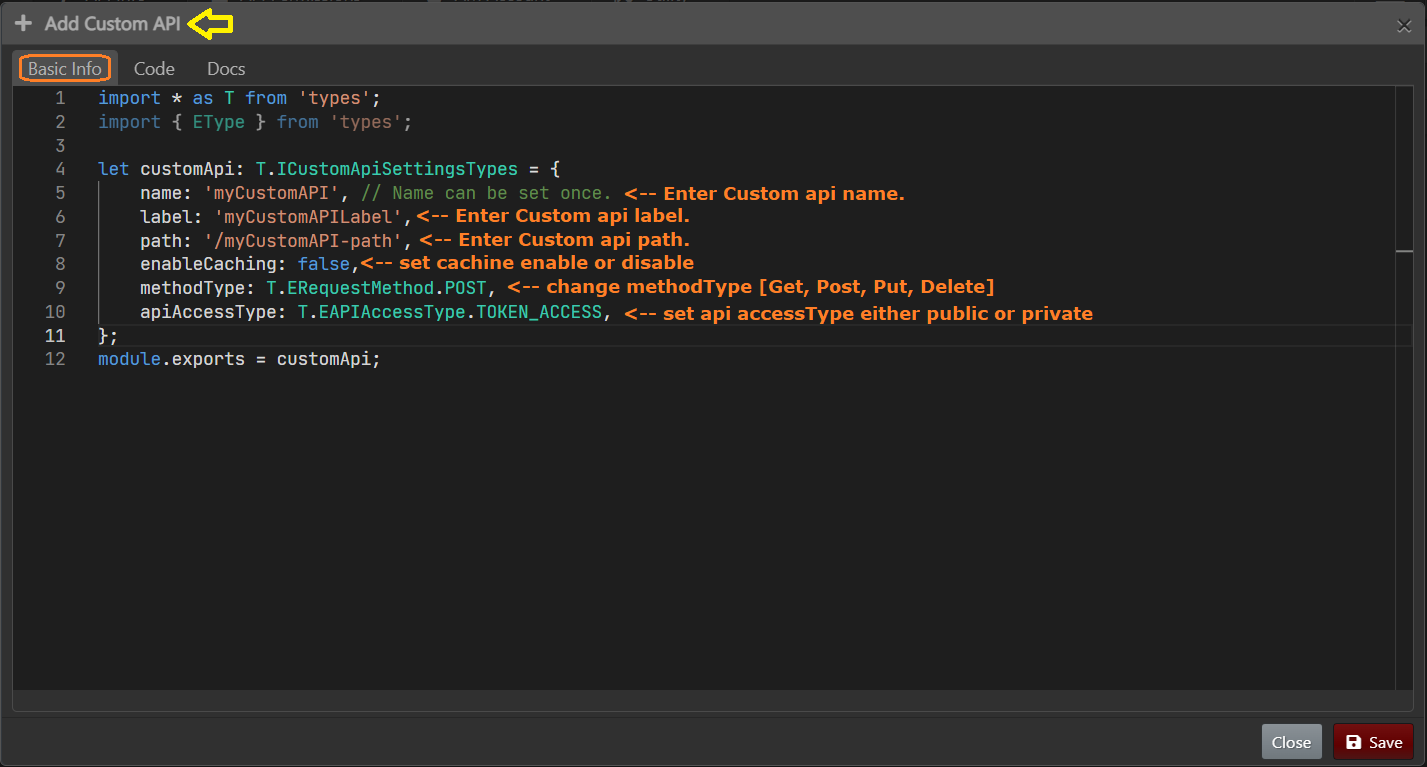
Here, you can specify custom API`s properties.
title: Custom API Settings description: Configure your custom APIs in API Maker—set routes, methods, caching, encryption, access type, error messages, and auth options.
- While add/update custom API you can see the custom API settings code in the
Basic Infotab.
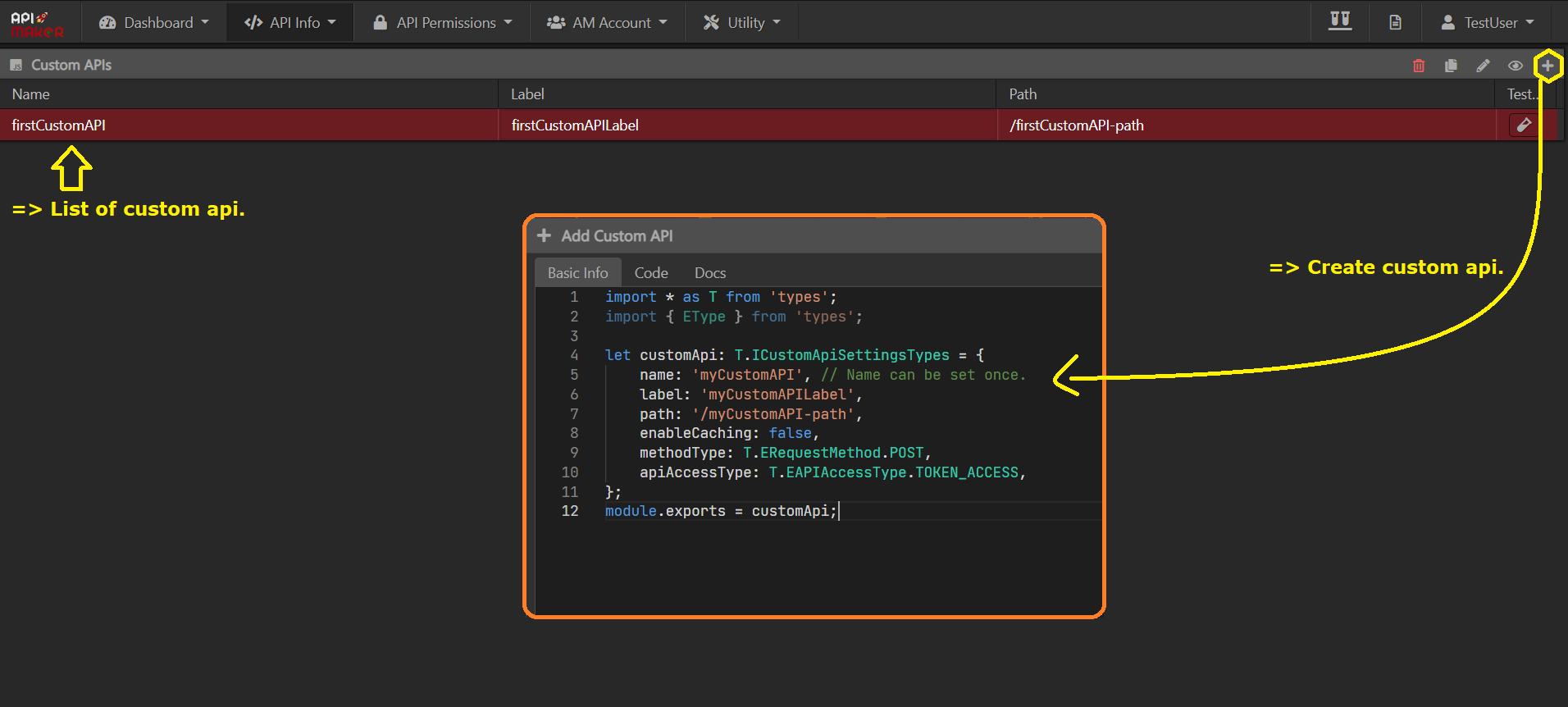
Custom APIs default settings code
Custom API Name
- The name of the custom API should be unique.
Label
- Custom APIs label is just a string that is shown everywhere.
Request method
- Set request method for the custom API.
- The request of that custom API should have given the method only.
- Supported request methods are
GET | POST | PUT | DELETE.
Path
- A custom API path is used to call the custom API.
- Add the path in the URL with the request method, and you will call that custom API.
- The path must be unique.
- The path and Request method combination must be unique.
Enable caching
To enable caching of a particular custom API, set enableCaching: true.
Reset cache on modification of
- We can reset the cache of the custom API if any modification happens in the given collection/table, custom API, or third party API using
resetCacheOnModificationOf. DB: instance_name:database_name:collection|table, if modify/delete data of this collection/table system will automatically reset the cache of this [Hello World] custom API.TP: api_bundle_name:api_version, if we hit any API of this version having [categoryRedis: EAPICategoryRedis.MODIFY_DATA], it will reset the cache of this [Hello World] custom API.CA: custom_api_name, if we hit this custom_api, it will reset the cache of this [Hello World] custom API.
Accept only encrypted data
- If you set the
acceptOnlyEncryptedDatavalue astrueAPI Maker will accept only the encrypted body, query params, and URL. - In the header provide
x-am-encrypted-payload: truewhen you setacceptOnlyEncryptedData: true.
Error list
- API Maker users can set a custom error list for each custom API.
- These errors will be listed in i18N, so you can map them in different languages.
In custom API settings
Throw error in custom API code
API access type
- There are two possible values of
apiAccessType. - When you set
IS_PUBLICthis collection's all APIs should be publicly available. - When you set
TOKEN_ACCESSthis collection's all APIs should require a token to access. - Provide API User token in the
x-am-authorizationheader.
Auth token info
- If you do not provide authTokenInfo it will take authTokenInfo from the default secret.
- If the authTokenInfo value is an empty array then provide only AM's API user's token in the
x-am-authorizationheader because we are overriding the default secret's authTokenInfo. In that, you have to provide API Maker's API user token in thex-am-authorizationheader.
- Now, if you set
authTokenType: T.EAuthTokenType.AM_DBand given required values in theauthTokenAMDBobject. The end user(who will use APIs) needs to provide the token in thex-am-user-authorizationheader. - The end user needs to create a token using the given instance, database, collection, usernameColumn, and passwordColumn values. Use the
getTokensystem API to get the token.
Custom API Code
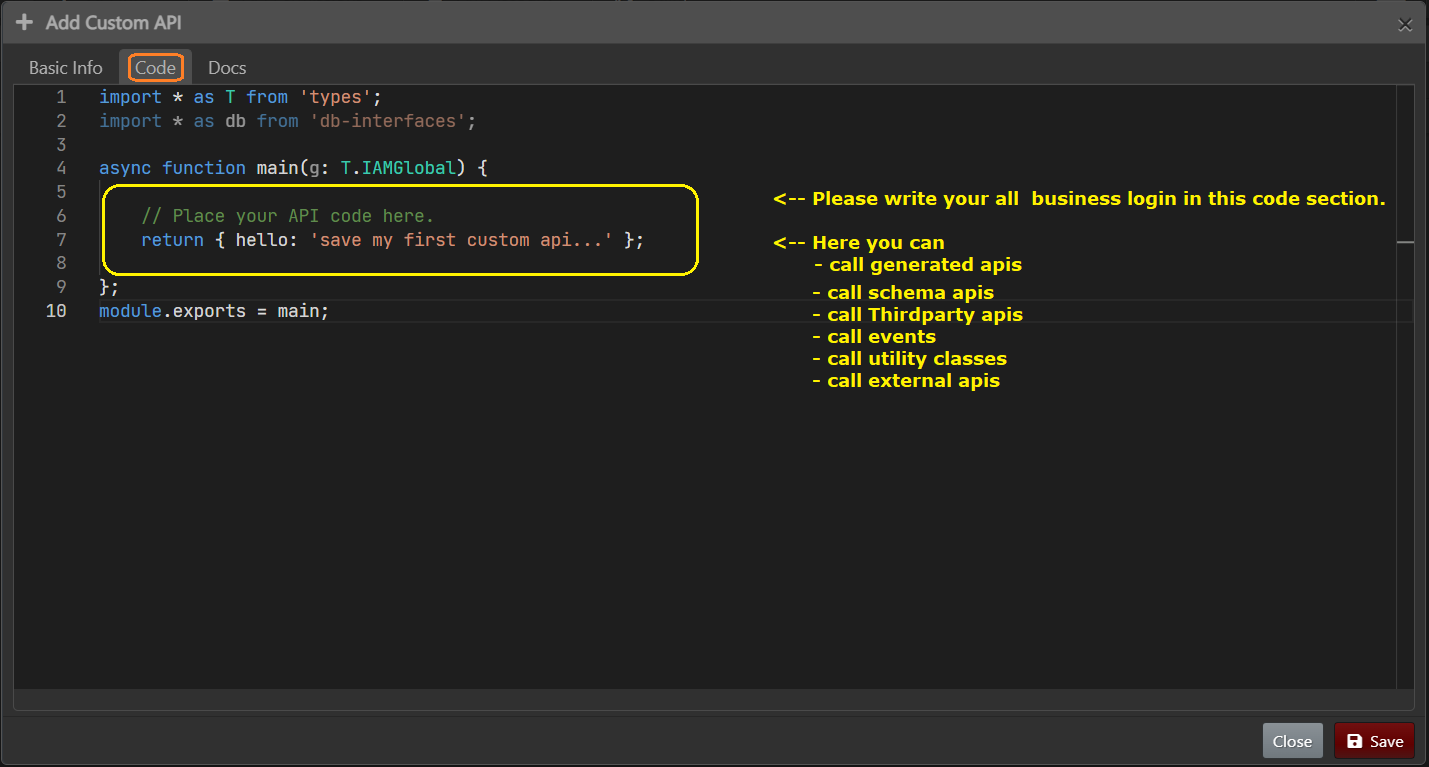
Here, you can call
Basic code
- Custom API has the async 'main' function. In which users will write their custom logic.
await, in custom API
- Write 'await' before the global object 'g' to write asynchronous code.
- Without 'await' it can be created problems.
true, in custom API
- Write 'true' that will help to non-stop execution of the custom API if that API gets an error response.
- If the user does not write the 'true' it will stop the execution and throw the error.
- One more use of 'true' is it will return whole response not only response data.
Throw error from custom API
- In custom API user can throw an error using the 'throw' keyword.
Get file custom API code
- You can create a custom API that will download files for the application user.
Custom API Docs
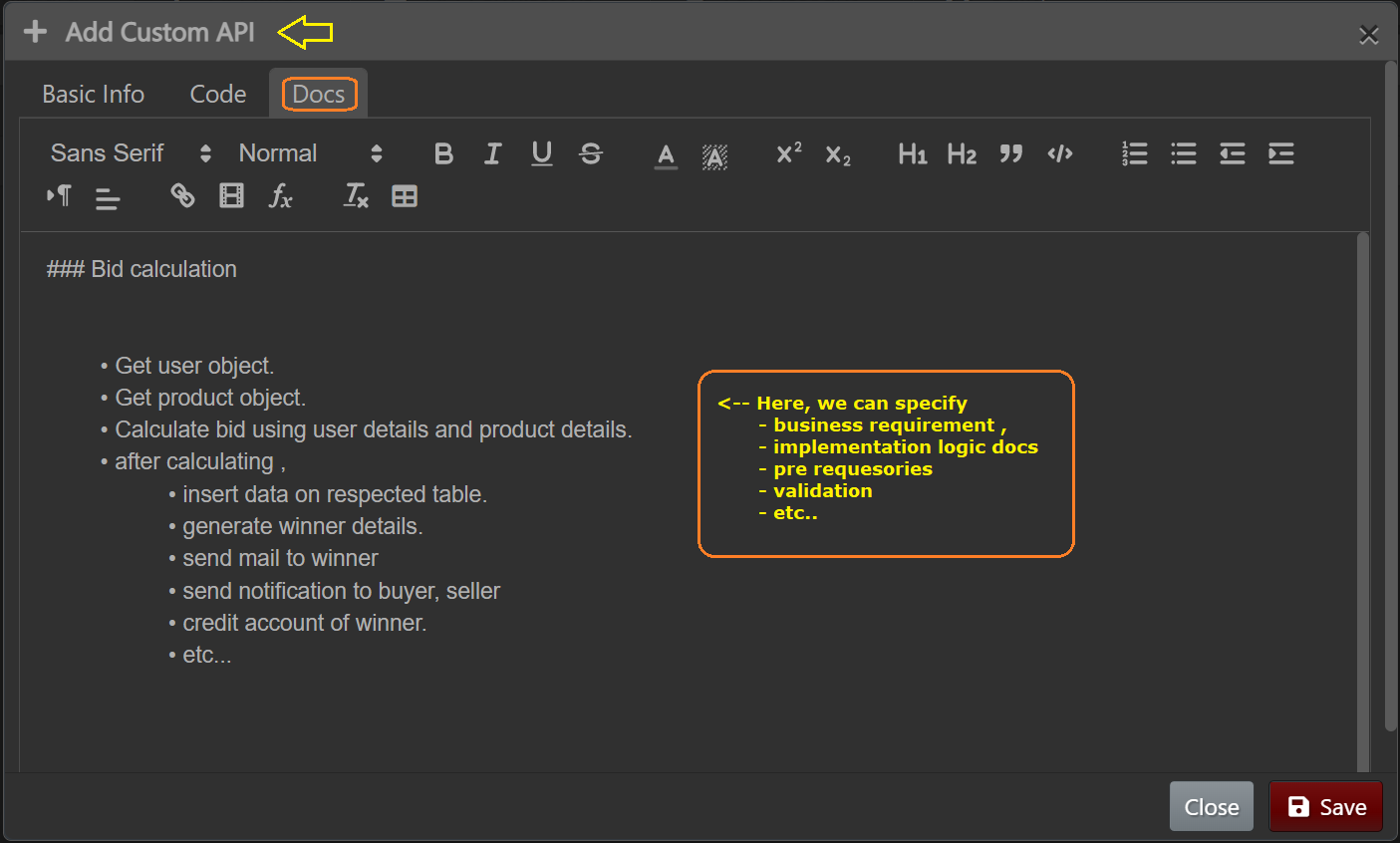
Here, you can specify